S Corporations represent an innovative and advantageous corporate structure for businesses of all sizes. With many benefits, such as avoiding double taxation, it is no surprise that S corporations are a popular choice amongst business owners.
This article offers a comprehensive breakdown of the S Corporation structure to provide readers with the necessary information they need to decide if this type of corporation will best suit their needs.
The complexities of setting up an S Corporation can be daunting; however, understanding its advantages and disadvantages can help make the process easier by providing guidance in making informed decisions.

This article breaks down each aspect of the S Corporation structure including requirements, setup processes, and other key points associated with running one successfully.
What Is An S Corporation?
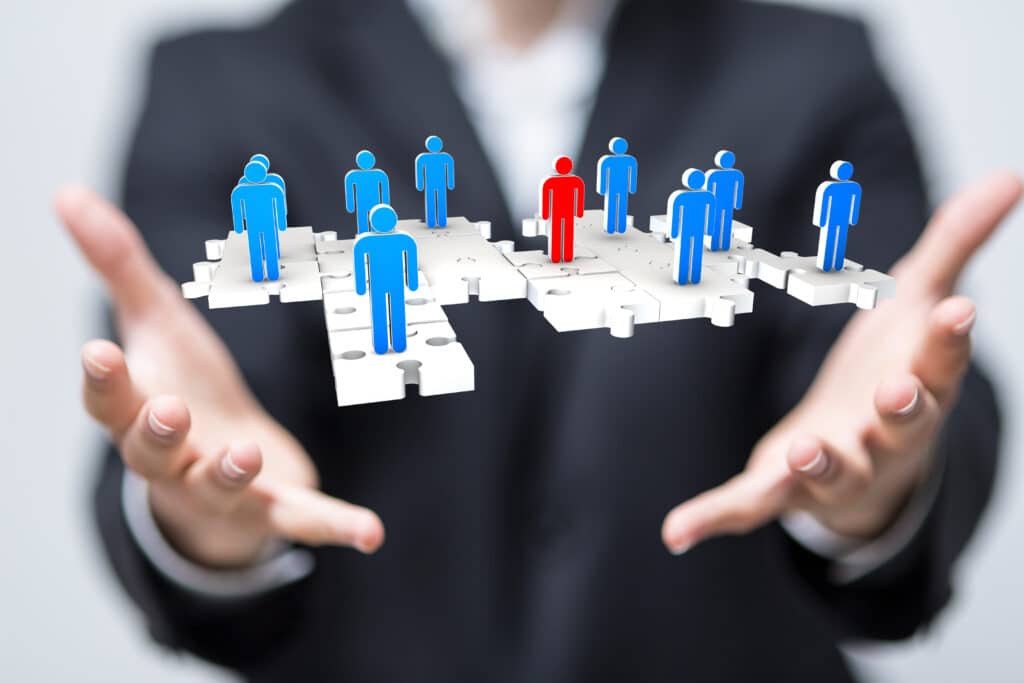
An S Corporation is a corporate structure that combines the taxation benefits of sole proprietorships and partnerships with the limited liability protection of corporations. This type of business entity offers shareholders legal rights to participate in business operations, as well as financial obligations for filing and compliance processes.
Take ABC Corp for example: it’s an S corporation started by three partners who wanted to have a separate legal identity from their individual businesses but also enjoy the tax advantages that come with being a pass-through entity. Each partner owns one-third share and has voting power over major decisions. The company operates in accordance with state-level regulations and files taxes annually at both federal and state levels.
The dissolution process of an S Corporation is similar to any other form of corporate organization – winding up activities, paying off debts, distributing remaining assets among owners, etc. After all these steps are taken care of, the final step would be submitting paperwork to dissolve the company’s legal status and officially cease its existence.
With this overview on S Corporations, we can now move onto discussing some common advantages associated with them.
Advantages Of S Corporations
S Corporations offer benefits for business owners that other types of corporations do not. The most obvious advantage is controlling ownership, as the S Corporation allows only one class of stock and limits shareholders to seventy-five or fewer.
Additionally, filing taxes and financial reporting requirements are often simpler than a C Corporation because all income flows through to the individual’s personal tax return.
Other advantages include:
- Business planning flexibility increases since decisions don’t have to pass through multiple levels of management.
- Insurance policies, employee benefits, and shareholder disputes may also be addressed more easily with an S Corporation structure.
- Operational costs can be lower in an S Corporation due to its limited liability status for debts incurred by the company.
The ability to manage certain aspects of a business without having to adhere to the restrictions imposed on larger companies makes S Corporations attractive options for small businesses seeking growth potential while minimizing risks associated with corporate entities.
Choose Incfile and form a C-corp by paying state fees only- No filing fees or other hidden charges!!
Disadvantages Of S Corporations
The advantages of an S Corporation are numerous and attractive, but it is important to be aware that there can also be disadvantages.
Double taxation, costs associated with formation and ongoing maintenance, limited control flexibility, and tax compliance requirements are some of the drawbacks that should be considered when making a decision about forming an S Corp.
As for double taxation, profits made by the corporation will generally first be taxed at the corporate level before being passed on to shareholders as qualified dividends or otherwise distributed from the corporation in order to avoid additional taxes.
In addition, owners must pay legal fees to ensure they understand all filing requirements and other necessary paperwork while navigating through the formation process.
Furthermore, S Corporations have restrictions in terms of how many shareholders are allowed (maximum 100) along with limits related to allowable types of business activities and profit distributions among those shareholders.
Who Can Form An S Corporation?
An S Corporation is like a dream come true for businesses looking to take their operations to the next level. It offers an unprecedented opportunity to reap tremendous benefits while taking advantage of legal and taxation strategies that can help you grow your business exponentially. Not only does it provide asset protection, but it also helps with capital investment and payroll taxes.
But before diving into the deep end, let’s look at who can form an S Corporation:
The eligibility criteria for forming an S Corporation are quite straightforward; in order to qualify, a company must file as a domestic C or S corporation entity through its state government’s department of revenue. Furthermore, the business structure needs to adhere to certain legal compliance standards set by both federal and state laws when selecting shareholders, directors, officers and employees.
In terms of financial requirements related to formation, there is often no minimum amount needed for capital investment nor any required payment upon filing. This makes the process more accessible than other corporate structures such as LLCs or Partnerships which require additional payments up front.
Additionally, some states allow corporations formed without substantial assets — meaning they don’t necessarily need large sums of money from investors prior to registration.

This flexibility allows entrepreneurs and companies alike unique opportunities for growth without having to put too much on the line financially. As long as all necessary documentation is filed correctly and tax obligations are met regularly, one’s business structure could be well-placed under the umbrella of an S Corporation – making them eligible for numerous potential advantages compared with other entities available in today’s market.
Requirements For Forming An S Corporation
Not every corporation or LLC is eligible for S-corporation status. The IRS imposes strict criteria, primarily aimed at smaller, domestically owned businesses. These criteria can be divided into three key categories: entity and structural requirements, shareholder qualifications, and filing obligations with both the state and IRS.
Entity and Structural Criteria
For starters, your business entity must be domestic, meaning it was formed or incorporated within the United States. Additionally, it must not fall into the category of ineligible corporations, which includes financial institutions, insurance companies, and domestic international sales corporations.
If your business fits into any of these categories, it’s wise to seek advice from tax and legal experts before pursuing S-corp status.
Shareholder Qualifications
Satisfying stringent requirements for shareholders (or members, in the case of an LLC) is essential. The most critical factor is that you must have no more than 100 shareholders to qualify as an S-corporation. Additionally, shareholders must meet the IRS definition of “eligible shareholders,” which includes individuals, certain trusts, or estates. Shareholders must also be U.S. citizens or legal residents. Partnerships and corporations are not eligible as shareholders.
Filing Procedures
To elect S-corp status, you’ll need to file Form 2553 with the IRS and fulfill any state-specific filing requirements. Unanimous shareholder consent is necessary, and you must meet the corporation and shareholder criteria mentioned earlier.
Form 2553 should be submitted no later than two months and 15 days after the start of the tax year for which you intend to make the election, or at any time during the preceding tax year. Detailed examples for calculating this deadline are available in the Form 2553 instructions.
Once Form 2553 is filed, your S-corporation will need to submit an annual tax return reflecting its status. Unlike traditional corporations that use Form 1120, S-corporations use federal Form 1120-S, which reports income, deductions, and payments.
State Tax Considerations
While S-corporation profits escape federal corporate income tax, state rules vary. Some states fully recognize S-corps, while others treat them as C-corps or impose additional criteria and filing obligations. You might need to file a separate state tax return for your S-corporation.
Tax Implications Of An S Corporation
S corporations are advantageous in terms of taxation and ownership rights, but there are still some legal risks that come with incorporating as an S corp.
The tax implications for owners of S corporations will depend on the filing process followed by the corporation itself. When it comes to deductions, profits from S corps can be split among members according to their respective profit sharing arrangements. This allows those who invest in an S corp to avoid double taxation—income taxes at both the individual level and at the corporate level.
In addition to providing shareholders with more flexibility when it comes to tax deductions, another major benefit of being an S corp is that all business losses incurred within a fiscal year may also be distributed proportionally amongst its members and deducted on each member’s personal income tax return.
Ownership rights and responsibilities outlined under Corporation Law further give individuals forming an s-corporation greater control over assets and decision making processes than other forms of businesses have.
The tax benefits associated with owning or operating an s-corp must always be weighed against any potential legal risks involved in setting up such a structure. While there are many advantages to forming an s-corporation, it’s important for potential business owners to understand how existing laws affect them before moving forward with incorporating as one.
Legal Aspects Of S Corporations
The legal aspects of S corporations are a fascinating subject to explore. It is like climbing an intricate mountain with many sides, each offering its own unique view of the corporation’s structure and function. As you ascend, you discover different paths that need to be taken in order for the corporation to achieve success.
Corporate Structure
One aspect of this journey involves understanding how an S corporation works from a structural point-of-view. This includes determining who serves as shareholders, directors, officers, and employees; what types of paperwork must be completed; and which laws apply. Knowing these details can help ensure compliance with applicable regulations while also providing maximum asset protection.
Estate Planning & Business Insurance
A second facet deals with estate planning and business insurance needs – both essential components when it comes to protecting corporate assets and ensuring financial stability in the future. Such tasks may require assistance from qualified professionals such as attorneys or accountants who specialize in these areas.
Financial Reporting & Tax Compliance
Finally, there are several key activities related to financial reporting and tax compliance that should be addressed on a regular basis (e.g., filing accurate returns). Additionally, employee benefits packages may need to be reviewed periodically to make sure they remain competitive within the marketplace.
Shareholders Management In S Corporation
The shareholders of an S Corporation have certain rights and responsibilities to be aware of. This ownership structure is unique compared to other business entities, as the profits are not taxed at the corporate level but instead passed through to the individual shareholders for taxation purposes.
The legal obligations that come with operating an S Corporation include understanding the applicable tax laws, creating and maintaining financial records, record keeping, compliance issues, and planning a dissolution process if necessary.
Shareholders should familiarize themselves with their rights in order to effectively manage an S Corporation. They may receive voting privileges on major decisions such as allocating dividends or increasing company debt levels. Furthermore, they must understand the relevant taxation strategies which will help them minimize their liability under IRS regulations.
Ownership interests can also be sold or transferred without prior approval from other parties or government agencies; however it is important to document these transactions properly in order to avoid any confusion down the line.
Create Your S-Corp in Minutes!When winding up operations of an S Corporation, it is essential to understand how this complex procedure works. Properly dissolving an entity requires following specific rules regarding filing documents with governmental bodies like local authorities and issuing final notices to creditors and vendors associated with the corporation.
Additionally, any remaining assets must be distributed among shareholders according to their percentage of ownership interest before its status is legally changed from active to inactive.
How To Dissolve An S Corporation
When it comes to dissolving an S Corporation, there are numerous legal requirements and procedures that must be followed.
The dissolution process begins with releasing assets such as banking accounts or any other property owned by the corporation. Additionally, all debts must be settled in order for the business structure to properly dissolve.
It is important to understand how taxation strategies may change when filing taxes after dissolving your S Corporation; thus corporate governance and compliance issues should also be addressed prior to officially closing up shop.
In addition to ensuring all of the above is taken care of, you will need to make sure all necessary paperwork has been filed with government agencies—especially if you plan on forming a new entity post-dissolution. This includes submitting documents like Articles of Dissolution or Certificate of Cancellation with state governments.
Furthermore, certain states may have additional forms that need to be submitted before officially dissolving your S Corporation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Are The Differences Between An S Corporation And A C Corporation?
When it comes to the differences between an S Corporation and a C Corporation, there are a few key points that need to be addressed.
The most notable of these include tax implications, state filing requirements, ownership restrictions, profit distributions, legal requirements and management structure.
Tax-wise, an S Corporation offers more flexibility in terms of taxation than a C Corporation does; as such, profits can be distributed without incurring double taxation.
Additionally, certain states may require additional paperwork for an S Corp compared to what is required for a regular corporation.
What Is The Difference Between A Sole Proprietorship And An S Corporation?
When deciding between a sole proprietorship and an S corporation, there are several factors to consider including potential tax implications for both entities, legal requirements associated with each type of business structure, employee benefits offered by either option, asset protection provided to shareholders in an S corp., the complexity of setting up and maintaining a corporate structure, filing deadlines specific to each entity, financial incentives available through an s-corp., as well as considerations regarding continuity of operations if ownership changes occur.
Is There A Minimum Or Maximum Number Of Shareholders For An S Corporation?
An S Corporation may have a minimum of one and maximum of 100 shareholders, depending on certain legal requirements.
It is important to note that the ownership structure comes with specific advantages such as liability protection and potential tax benefits.
Additionally, it also enables more equity options for each shareholder in regards to profit sharing, filing requirements, and rights associated with their shares.
Are There Any Restrictions On Who Can Be A Shareholder Of An S Corporation?
The potential to become a shareholder of an s corporation comes with both exciting opportunities and demanding restrictions. Aspiring shareholders must consider tax implications, income requirements, corporate governance, asset protection, capital contributions, shareholder benefits and the legal structure in order to determine their eligibility for such an enterprise.
Furthermore, those interested need to be aware of the strict filing requirements that come along with the investment; making sure all forms are correctly filed and submitted within the given deadline is essential for success.
Conclusion
The S Corporation is a powerful business structure that can provide many advantages to its owners. It’s important for anyone considering this type of setup to understand the differences between it and other types of corporations, as well as who may be eligible to become shareholders in an S Corp.
The symbolism associated with this type of business formation speaks volumes about the stability and potential success that it offers: think of each shareholder like one spoke on a wheel, all connected and working together to turn the wheel towards greater growth and profits.
This collective effort combined with thoughtful planning presents an exciting opportunity for those looking to maximize their business goals.